Bringing shape into focus: Assessing differences between blades and bladelets and their technological significance in 3D form
Abstract
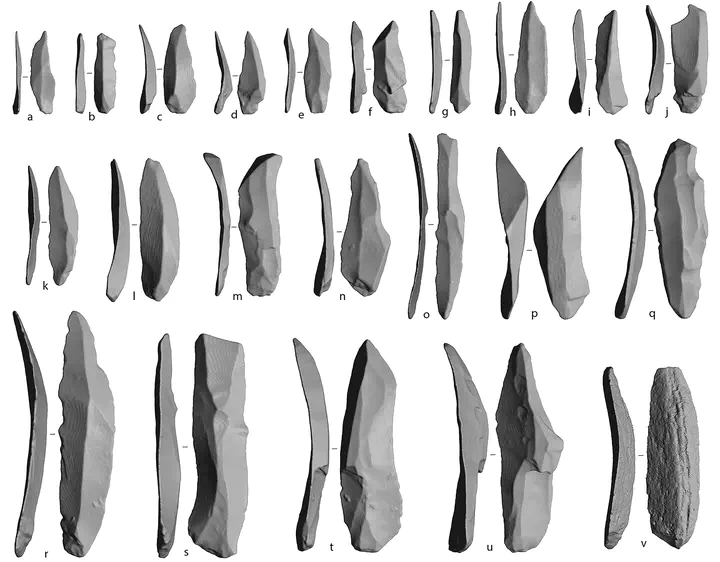
Laminar technologies were adopted by Paleolithic foragers to produce a variable range of stone implements. Archaeologists have reconstructed the different reduction procedures involved in the production of laminar stone tools, often underlying a separation between the bigger blanks (i.e., blades) and smaller bladelets. However, these two blank types are in most cases poorly defined, as their classification typically relies on arbitrary size thresholds that do not consider blank shape, which is a fundamental component of tool production and function. In this study, we investigate whether traditional classifications of blades and bladelets are morphologically and technologically meaningful. For this purpose, we employ a three-dimensional geometric morphometric approach on a large sample of complete blanks retrieved from one of the earliest laminar industries assigned to modern humans in southern Europe: the Protoaurignacian from Fumane Cave. We rely on a cutting-edge protocol for acquiring virtual 3D meshes of stone tools using micro-computed tomography. This novel approach allows us to scan large quantities of small lithics in a short period of time and without the typical technical problems associated with scanning small objects. After calculating the principal components of shape variation, we explore differences and similarities across the dataset using linear discriminant analysis and analysis of variance. Our multivariate study highlights distinct morphological tendencies across blades and bladelets that are however better framed when the technological organization of Protoaurignacian stone knapping is taken into consideration. Overall, our results demonstrate that virtual analysis of stone tool shape can help elucidate aspects of lithic technology and its implications for past human behavior.