Biography
Welcome to my website! I am a Global Marie Skłodowska‑Curie Fellow at the Department of Anthropology at New York University and the Interdisciplinary Center for Archaeology and Evolution of Human Behavior (ICArEHB) at the University of Algarve, leading the RStone project: Population interconnectivity and technological trajectories in southern Africa during MIS3 through replicable lithic analysis. This fellowship allows me to develop standardized, quantitative methods for lithic analysis, apply 3D visualization techniques to MIS3 assemblages across southern Africa, and test hypotheses about cultural fragmentation during the MIS3.
In parallel, I am an Associated Researcher at the Institute for Archaeological Sciences at the University of Tübingen, where I teach courses on Stone Age Technology, the Prehistory of Mediterranean Europe, and 3D Applications in Lithic Analysis.
From 2020 to 2025, I led the DFG-funded project Investigating Early Upper Paleolithic technological variability and cultural dynamics south of the Alps. This research explored how cultural transmission and environmental factors shaped the lifeways of foragers along the Italian Peninsula between 42,000 and 36,000 years ago, combining traditional archaeological methods, experimental approaches, and advanced 3D analyses.
I am also committed to advancing Open Science. I have created open-access repositories for the Early Upper Paleolithic, providing researchers worldwide with high-resolution 3D models and attribute-based datasets of stone tool assemblages—resources designed to foster global collaboration and improve reproducibility in archaeological research.
In 2025, I was elected as a regular board member of the European Society for the Study of Human Evolution (ESHE). In this role, I contribute to fostering interdisciplinary collaboration in human evolution research, supporting early-career researchers, and promoting public engagement with the study of human origins.
- Paleolithic Archaeology
- Lithic Technology
- Experimental Archaeology
- Cultural Transmission
- Open Science
- 3D Visualization
- Science Communication
PhD in Paleolithic Archaeology, 2019
University of Tübingen
MA in Quaternary, Prehistory, and Archaeology, 2015
University of Ferrara
BA in Cultural Heritage Sciences, 2013
University of Rome II
Skills
Featured Publications
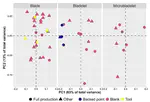
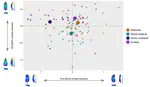
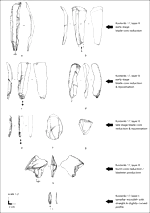
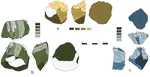
The appearance of the Protoaurignacian in Europe around 42,000 years ago is widely believed to result from a major dispersal of anatomically modern Homo sapiens out of the Levant, a view primarily supported by perceived similarities between Mediterranean Protoaurignacian and Levantine Ahmarian stone tools. However, no quantitative technological comparison has yet thoroughly tested this connection. Here, we present the first systematic evaluation of lithic technology from Protoaurignacian assemblages in Italy and from the northern Ahmarian and post-Ahmarian layers at the reference sequence of Ksar Akil (Lebanon). Using attribute analysis and multivariate statistics, we assessed technological similarities and differences across different stages of the core reduction sequence. Our results demonstrate very limited affinities and distinct technological trajectories between the two regions. While the northern Ahmarian at Ksar Akil is characterized by bidirectional volumetric core reduction aimed at blade production, the Protoaurignacian exhibits a strong emphasis on bladelet production from unidirectional cores. Although lithic miniaturization trends are observed in both regions, the post-Ahmarian layers at Ksar Akil primarily produced twisted bladelets from burins and carinated cores—a feature uncommon in the Protoaurignacian. These findings challenge the hypothesis of a Levantine origin for the Protoaurignacian and, more broadly, suggest that technological convergence—driven by the growing importance of multicomponent projectile technology and increased mobility—played a central role. Thus, our study underscores the need to reconsider diffusionist explanations and emphasizes the central role of internal cultural innovation among foraging groups settled in different regions of the Old World in shaping the emergence of the Upper Paleolithic.
The paper has been featured in several national and international news outlets, including:
- Discover Magazine (English)
- Geo.fr (French)
- Pikaia.eu (Italian)
- Phys.org (English)
- Science & Vie (French)
- Stuttgarter Zeitung (German)
The original press release is from the University of Tuebingen.
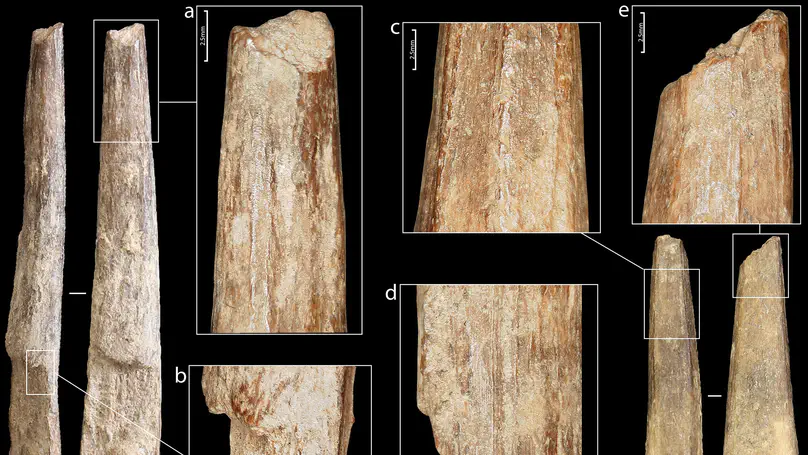

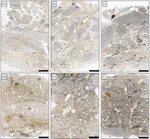
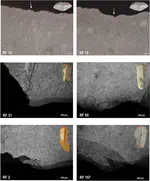
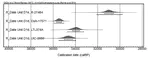
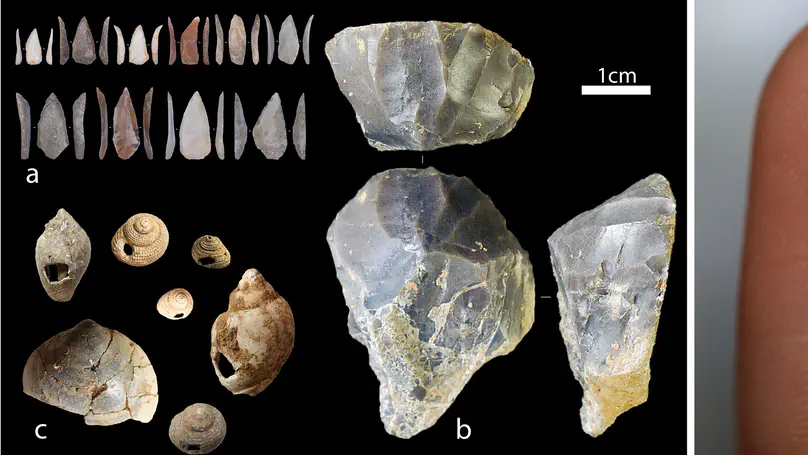
Riparo Bombrini is a collapsed rockshelter within the Balzi Rossi site complex, located at the intersection of the Maritime Alps, Northern Apennines, and Ligurian Sea. This unique environmental setting served as a crucial biogeographical corridor for human mobility along the Liguro-Provençal Arc during the Paleolithic. Multidisciplinary research at Bombrini identified three archaeological layers (i.e., A2, A1, and A0) overlying a semi-sterile Mousterian level. This paper explores the internal variability of the Protoaurignacian by analyzing lithic assemblages from layers A2 and A1, as well as a previously undescribed Early Aurignacian assemblage from layer A0. An analysis of assemblage integrity, lithic technology, and raw material procurement reveals distinct mobility and land-use strategies, despite technological uniformity. Remarkably, lithic production and use in both Protoaurignacian and Early Aurignacian layers frequently involved exogenous materials sourced from distances exceeding 150 km, with some reaching up to 450 km, spanning from the Rhône Valley to the Central Apennines. Variability in the procurement distance of discarded lithics and their changing reduction intensities highlight distinct patterns of logistical and residential mobility. Comparative analysis with regional sites indicates that foragers possessed sophisticated territorial knowledge, challenging the traditional view of the Protoaurignacian as the outcome of pioneering groups entering unfamiliar landscapes.
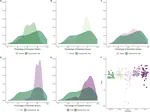
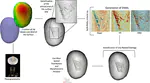
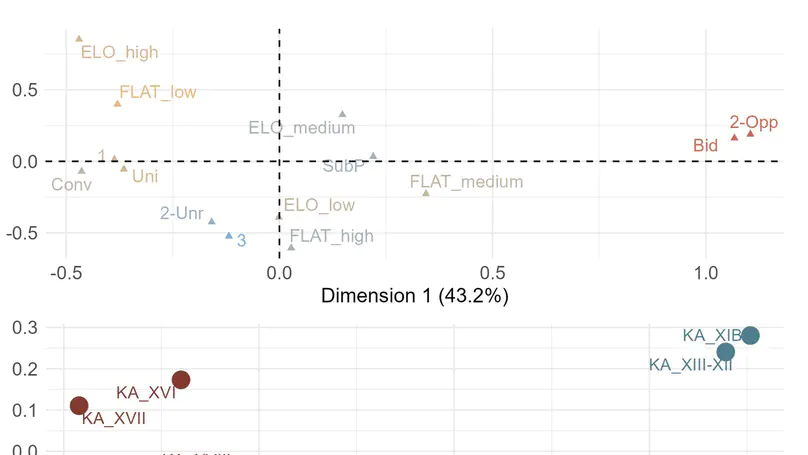
The Aurignacian is the first European technocomplex assigned to Homo sapiens recognized across a wide geographic extent. Although archaeologists have identified marked chrono-cultural shifts within the Aurignacian mostly by examining the techno-typological variations of stone and osseous tools, unraveling the underlying processes driving these changes remains a significant scientific challenge. Scholars have, for instance, hypothesized that the Campanian Ignimbrite (CI) super-eruption and the climatic deterioration associated with the onset of Heinrich Event 4 had a substantial impact on European foraging groups. The technological shift from the Protoaurignacian to the Early Aurignacian is regarded as an archaeological manifestation of adaptation to changing environments. However, some of the most crucial regions and stratigraphic sequences for testing these scenarios have been overlooked. In this study, we delve into the high-resolution stratigraphic sequence of Grotta di Castelcivita in southern Italy. Here, the Uluzzian is followed by three Aurignacian layers, sealed by the eruptive units of the CI. Employing a comprehensive range of quantitative methods-encompassing attribute analysis, 3D model analysis, and geometric morphometrics-we demonstrate that the key technological feature commonly associated with the Early Aurignacian developed well before the deposition of the CI tephra. Our study provides thus the first direct evidence that the volcanic super-eruption played no role in this cultural process. Furthermore, we show that local paleo-environmental proxies do not correlate with the identified patterns of cultural continuity and discontinuity. Consequently, we propose alternative research paths to explore the role of demography and regional trajectories in the development of the Upper Paleolithic.
The paper has been featured in several national and international news outlets, including:
- Earth.com (English)
- LaNotaDelDia.mx (Spanish)
- LaRepubblica.it (Italian)
- Lenta.ru (Russian)
- Phys.org (English)
- PoskoNews.com (Indonesian)
The original press releases are from the University of Tuebingen in English and the University of Siena in Italian.
Publications
Recent & Upcoming Talks
Projects
Contact Me
- Burgsteige 11, Tübingen, DE 72070
- DM Me