Publications
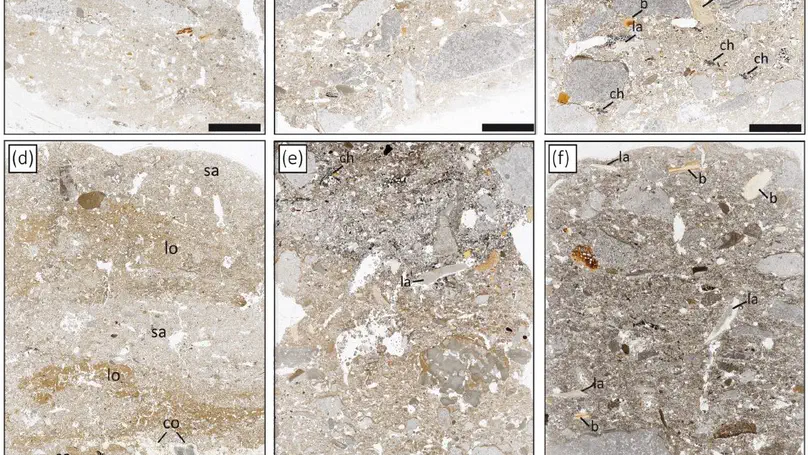

Fumane Cave contains a sequence of natural and anthropogenic deposits documenting key transitions in the Paleolithic of Northern Italy. Open questions remain concerning the stratigraphic integrity, the formation processes, postdepositional alterations, and paleoclimatic implications of the sedimentary record.We examine these aspects through an extensive investigation based on field descriptions and micromorphological analysis of thin sections sampled during the last 25 years of excavations. Major components of the sediments are carbonate sands and limestone rubble originating from the physical breakdown of the cave roof and walls. Limited amounts of mica and quartz grains attest to weak eolian inputs. Sediments contain anthropogenic features and variable amounts of charcoal, bone, and lithic artifacts reflecting different uses of the site. Cryoturbation features observed in the field suggest an increased intensity of frost mainly after the accumulation of unit A2. This unit as well as unit A6 also show increased abundance of silt and clay cappings under the microscope, probably reflecting higher rates of snowfall and percolating meltwater during colder periods of the Last Glacial. However, limited expression of micromorphological features related to frost suggests rather modest changes in climate during the accumulation of the sequence. Overall, field descriptions and the micromorphological approach mostly corroborate the stratigraphic integrity of the sequence, underlining the high value of Fumane Cave as an archive of the late Middle to early Upper Paleolithic in Southern Europe.
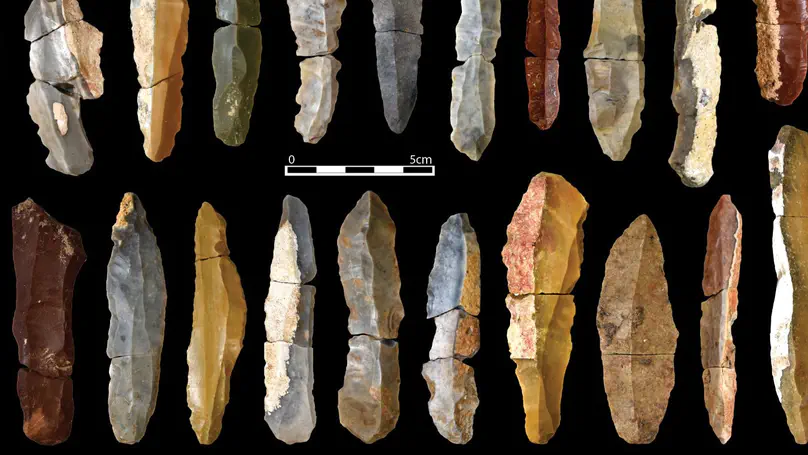

High-resolution stratigraphic frameworks are crucial for unraveling the biocultural processes behind the dispersals of Homo sapiens across Europe. Detailed technological studies of lithic assemblages retrieved from multi-stratified sequences allow archaeologists to precisely model the chrono-cultural dynamics of the early Upper Paleolithic. However, it is of paramount importance to verify the integrity of these assemblages before building explanatory models of cultural change. In this study, multiple lines of evidence suggest that the stratigraphic sequence of Fumane Cave in northeastern Italy experienced minor post-depositional reworking, establishing it as a pivotal site for exploring the earliest stages of the Aurignacian. By conducting a systematic search for break connections between blade fragments and applying spatial analysis techniques, we identified three well-preserved areas of the excavation containing assemblages suitable for renewed archaeological investigations. Subsequent technological analyses, incorporating attribute analysis, reduction intensity, and multivariate statistics, have allowed us to discern the spatial organization of the site during the formation of the Protoaurignacian palimpsest A2–A1. Moreover, diachronic comparisons between three successive stratigraphic units prompted us to reject the hypothesis of techno-cultural continuity of the Protoaurignacian in northeastern Italy after the onset of the Heinrich Event 4. Based on the variability of the lithic and osseous artifacts, the most recent assemblage analyzed, D3b alpha, is now ascribed to the Early Aurignacian, aligning the evidence from Fumane with the current understanding of the development of the Aurignacian across Europe. Overall, this study demonstrates the high effectiveness of the break connection method when combined with detailed spatial analysis and lithic technology, providing a methodological tool particularly amenable to be applied to sites excavated in the past with varying degrees of recording accuracy.
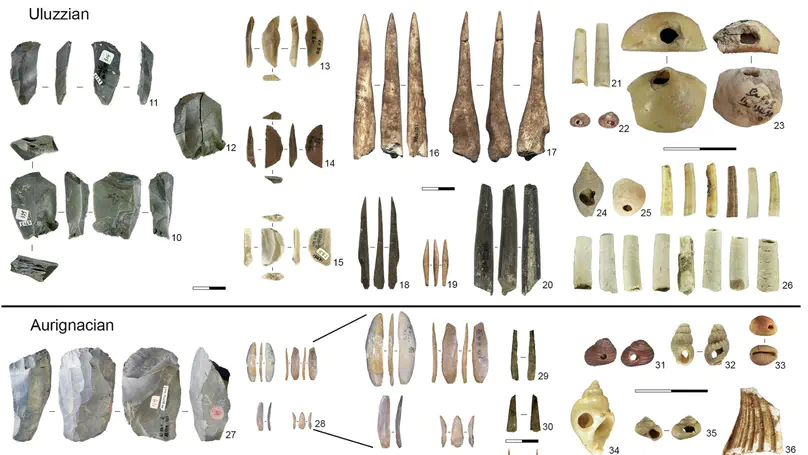

The process by which Palaeolithic Europe was transformed from a Neanderthal-dominated region to one occupied exclusively by Homo sapiens has proven challenging to diagnose. A blurred chronology has made it difficult to determine when Neanderthals disappeared and whether modern humans overlapped with them. Italy is a crucial region because here we can identify not only Late Mousterian industries, assumed to be associated with Neanderthals, but also early Upper Palaeolithic industries linked with the appearance of early H. sapiens, such as the Uluzzian and the Aurignacian. Here, we present a chronometric dataset of 105 new determinations (74 radiocarbon and 31 luminescence ages) from four key southern Italian sites: Cavallo, Castelcivita, Cala, and Oscurusciuto. We built Bayesian-based chronometric models incorporating these results alongside the relative stratigraphic sequences at each site. The results suggest; 1) that the disappearance of Neanderthals probably pre-dated the appearance of early modern humans in the region and; 2) that there was a partial overlap in the chronology of the Uluzzian and Protoaurignacian, suggesting that these industries may have been produced by different human groups in Europe.
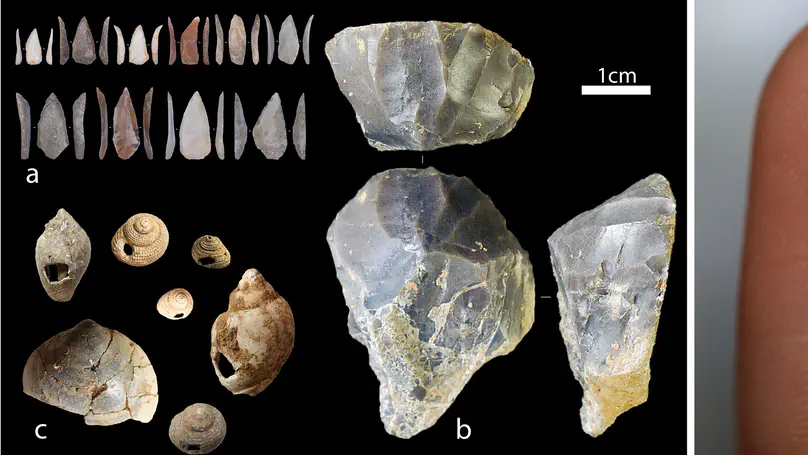
The Aurignacian is the first European technocomplex assigned to Homo sapiens recognized across a wide geographic extent. Although archaeologists have identified marked chrono-cultural shifts within the Aurignacian mostly by examining the techno-typological variations of stone and osseous tools, unraveling the underlying processes driving these changes remains a significant scientific challenge. Scholars have, for instance, hypothesized that the Campanian Ignimbrite (CI) super-eruption and the climatic deterioration associated with the onset of Heinrich Event 4 had a substantial impact on European foraging groups. The technological shift from the Protoaurignacian to the Early Aurignacian is regarded as an archaeological manifestation of adaptation to changing environments. However, some of the most crucial regions and stratigraphic sequences for testing these scenarios have been overlooked. In this study, we delve into the high-resolution stratigraphic sequence of Grotta di Castelcivita in southern Italy. Here, the Uluzzian is followed by three Aurignacian layers, sealed by the eruptive units of the CI. Employing a comprehensive range of quantitative methods-encompassing attribute analysis, 3D model analysis, and geometric morphometrics-we demonstrate that the key technological feature commonly associated with the Early Aurignacian developed well before the deposition of the CI tephra. Our study provides thus the first direct evidence that the volcanic super-eruption played no role in this cultural process. Furthermore, we show that local paleo-environmental proxies do not correlate with the identified patterns of cultural continuity and discontinuity. Consequently, we propose alternative research paths to explore the role of demography and regional trajectories in the development of the Upper Paleolithic.
The paper has been featured in several national and international news outlets, including:
- Ancientpages.com (English)
- Earth.com (English)
- GreenReport.it (Italian)
- IlGiornale.ch (Italian)
- Knowridge.com (English)
- LaNotaDelDia.mx (Spanish)
- LaRepubblica.it (Italian)
- Lenta.ru (Russian)
- MeteoWeb.eu (Italian)
- Phys.org (English)
- PoskoNews.com (Indonesian)
- RedenginePress.com (English)
- SSPDaily.com (English)
- TechAndSciencePost.com (English)
- WorldCulturalHeritageVoices.org (English)
The original press releases are from the University of Tuebingen in English and the University of Siena in Italian.
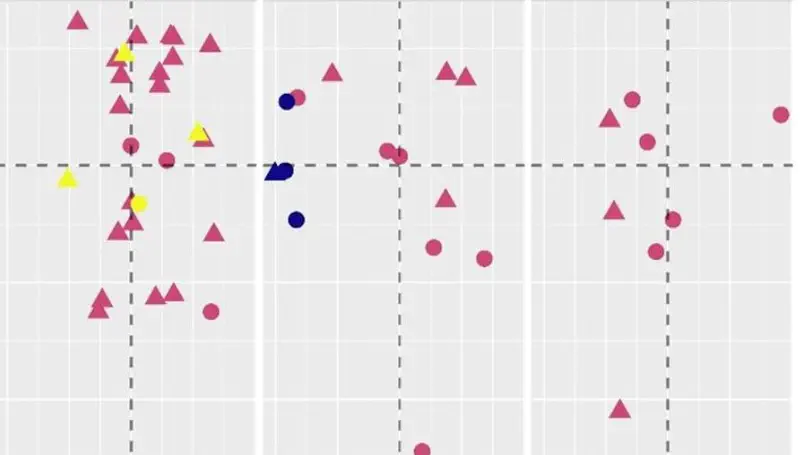
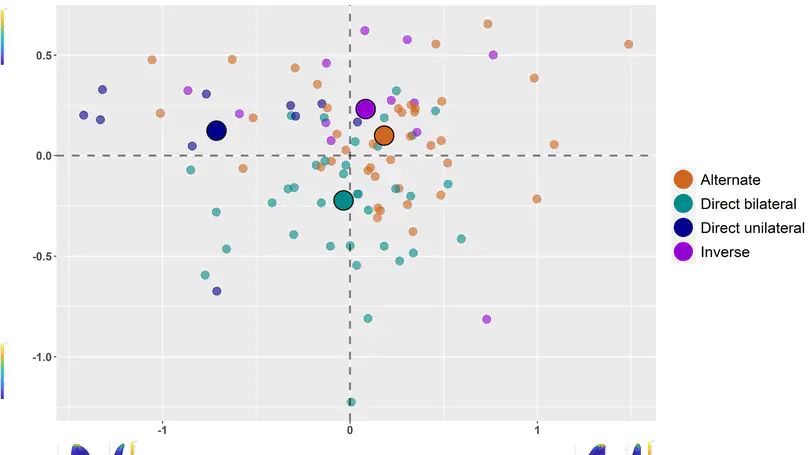
In this paper, we apply a two-dimensional (2D) Geometric morphometric analysis to a sample of Epigravettian lithic artefacts with the aim of assessing the potential of such an approach to study Epigravettian lithic assemblages. The lithic sample comes from layer 9c2 (Evolved Epigravettian, Upper Palaeolithic, about 18,000-19,000 years ago) of Grotta Paglicci (Apulia, southern Italy). After extracting the outline coordinates from high-resolution images using the software DiaOutline, we conduct Elliptic Fourier Analysis, Principal Component Analysis, and Linear Discriminant Analysis in the R package Momocs to investigate the internal variability of the sample. Shape analysis confirms that 1) the production of microbladelets was not linked to a dedicated reduction sequence and 2) the modification of blanks into backed points followed a rather standardised stone tool design. The result opens interesting perspectives for the routine implementation of 2D shape analyses complementary to the classical technological ones.
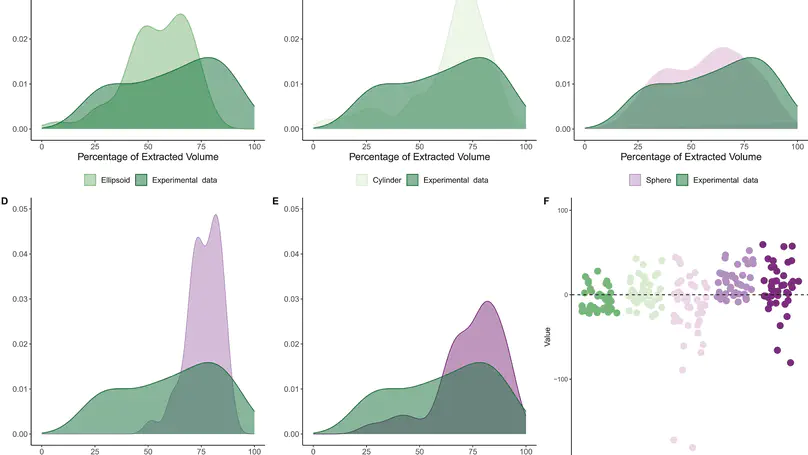
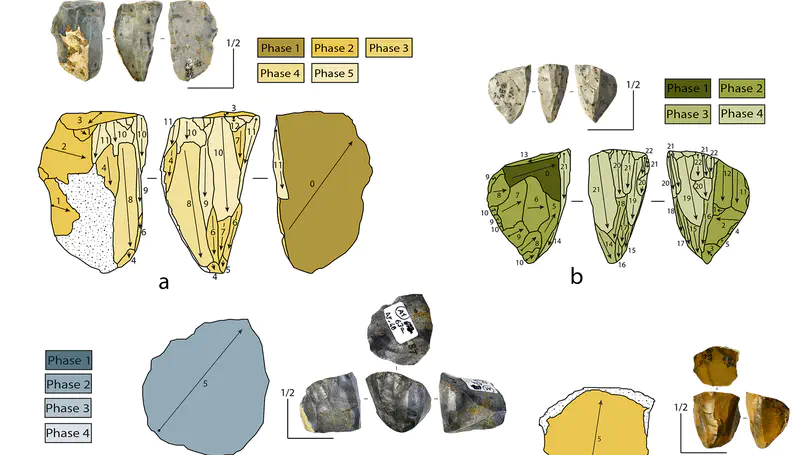
This paper investigates core reduction intensity in the early Protoaurignacian lithic assemblage from Fumane Cave in northeastern Italy. Reduction intensity serves as a key tool to characterize blank selection strategies, raw material management, and the variability of knapping strategies throughout the reduction sequence by reconstructing the operatory field of core assemblages. Finally, it also aids in addressing the relationship between blades and bladelets, providing valuable insights into the behavioral and chrono-cultural significance of laminar productions within the Aurignacian technocomplex. To achieve these research goals, experimental work employing 3D scanning technology was conducted. This facilitated the comparison of different methods and variables for measuring reduction intensity, including the percentage of non-cortical surface, the Scar Density Index (SDI), and a novel adaptation of the Volumetric Reconstruction Method (VRM). Results demonstrate the effectiveness and potential of adapting the VRM for the study of reduction intensity in Upper Paleolithic laminar cores, and the provided R scripts and datasets will enable this method to be applied to other contexts with minimal need for modification to the workflow. Analysis of reduction intensity measures applied to the Protoaurignacian assemblage from Fumane Cave reveals slight variations based on factors such as the abundance and proximity of selected raw materials for blank production. Notably, the most prevalent raw material variety, the Maiolica, yields a higher number of less reduced cores, while reduction levels across all cores discarded at the site remain relatively high. The observed variability in the operatory field and the interrelation between blade and bladelet productions underscore the complexity and flexibility of Protoaurignacian behavior. This inherent complexity challenges any definitive separation between the operatory fields of blade and bladelet productions. These findings are particularly important to emphasize the importance of considering reduction intensity when examining technological variability and human behavior in Aurignacian studies. The proposed adaptation of the VRM and the effective combination with other measures of reduction, promises to allow future research to incorporate reduction intensity as a vital temporal component within studies on stone tool production. This integration offers a pathway to enhancing our understanding of the adaptive behaviors exhibited by Homo sapiens across diverse ecological settings and provides a clearer framework for better framing the development of the Upper Paleolithic.
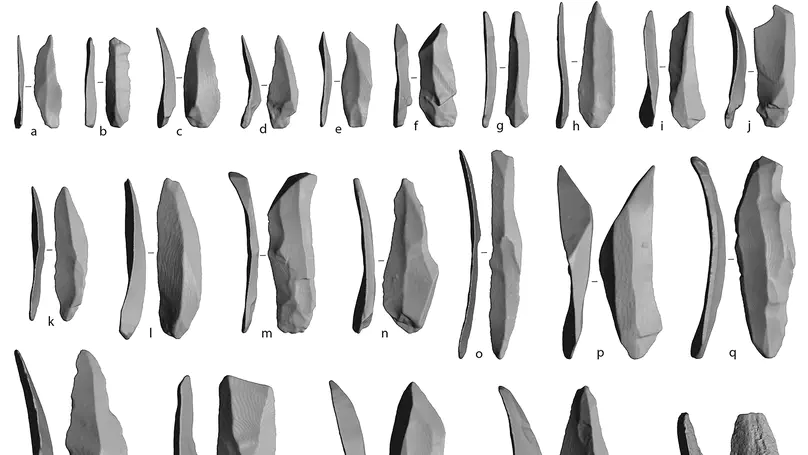
Laminar technologies were adopted by Paleolithic foragers to produce a variable range of stone implements. Archaeologists have reconstructed the different reduction procedures involved in the production of laminar stone tools, often underlying a separation between the bigger blanks (i.e., blades) and smaller bladelets. However, these two blank types are in most cases poorly defined, as their classification typically relies on arbitrary size thresholds that do not consider blank shape, which is a fundamental component of tool production and function. In this study, we investigate whether traditional classifications of blades and bladelets are morphologically and technologically meaningful. For this purpose, we employ a three-dimensional geometric morphometric approach on a large sample of complete blanks retrieved from one of the earliest laminar industries assigned to modern humans in southern Europe: the Protoaurignacian from Fumane Cave. We rely on a cutting-edge protocol for acquiring virtual 3D meshes of stone tools using micro-computed tomography. This novel approach allows us to scan large quantities of small lithics in a short period of time and without the typical technical problems associated with scanning small objects. After calculating the principal components of shape variation, we explore differences and similarities across the dataset using linear discriminant analysis and analysis of variance. Our multivariate study highlights distinct morphological tendencies across blades and bladelets that are however better framed when the technological organization of Protoaurignacian stone knapping is taken into consideration. Overall, our results demonstrate that virtual analysis of stone tool shape can help elucidate aspects of lithic technology and its implications for past human behavior.
Protoaurignacian foragers relied heavily on the production and use of bladelets. Technotypological studies of these implements have provided insights into crucial aspects of cultural variability. However, new technologies have seldom been used to quantify patterns of stone tool design. Taking advantage of a new scanning protocol and open-source software, we conduct the first 3D analysis of a Protoaurignacian assemblage, focusing on the selection and modification of blades and bladelets. We study a large dataset of complete blanks and retouched tools from the early Protoaurignacian assemblage at Fumane Cave in northeastern Italy. Our main goal is to validate and refine previous techno-typological considerations employing a 3D geometric morphometrics approach complemented by 2D analysis of cross-section outlines and computation of retouch angle. The encouraging results show the merits of the proposed integrated approach and confirm that bladelets were the main focus of stone knapping at the site. Among modified bladelets, various retouching techniques were applied to achieve specific shape objectives. We suggest that the variability observed among retouched bladelets relates to the design of multi-part artifacts that need to be further explored via renewed experimental and functional studies.

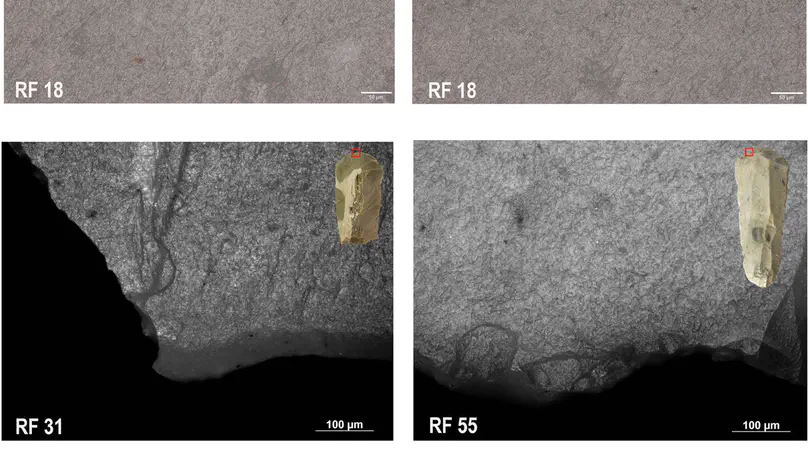
Here, we present a new method to scan a large number of lithic artefacts using three-dimensional scanning technology. Despite the rising use of high-resolution 3D surface scanners in archaeological sciences, no virtual studies have focused on the 3D digitization and analysis of small lithic implements such as bladelets, microblades, and microflakes. This is mostly due to difficulties in creating reliable 3D meshes of these artefacts resulting from several inherent features (i.e., size, translucency, and acute edge angles), which compromise the efficiency of structured light or laser scanners and photogrammetry. Our new protocol StyroStone addresses this problem by proposing a step-by-step procedure relying on the use of micro-computed tomographic technology, which is able to capture the 3D shape of small lithic implements in high detail. We tested a system that enables us to scan hundreds of artefacts together at once within a single scanning session lasting a few hours. As also bigger lithic artefacts (i.e., blades) are present in our sample, this protocol is complemented by a short guide on how to effectively scan such artefacts using a structured light scanner (Artec Space Spider). Furthermore, we estimate the accuracy of our scanning protocol using principal component analysis of 3D Procrustes shape coordinates on a sample of meshes of bladelets obtained with both micro-computed tomography and another scanning device (i.e., Artec Micro). A comprehensive review on the use of 3D geometric morphometrics in lithic analysis and other computer-based approaches is provided in the introductory chapter to show the advantages of improving 3D scanning protocols and increasing the digitization of our prehistoric human heritage.
Endscrapers are specialized tools that are usually recovered in great quantities in every Upper Paleolithic site in Europe. Although they make their first ephemeral appearance in the Middle–late Middle Paleolithic transitional technocomplexes, endscrapers commonly appear in toolkits from initial and early Upper Paleolithic traditions onwards. Nevertheless, endscrapers and, in general, domestic tools have attracted relatively little attention in debates revolving around the significance of technological change, tool function, and tool specialization after the end of the Middle Paleolithic. With the aim to overcome this paucity of information, here, we present the results of a techno-functional study performed on the large endscraper assemblage recovered from the early and late Protoaurignacian layers at Fumane Cave in northeastern Italy. We analyzed these artifacts using technological, morpho-metrical, typological, and functional approaches. Despite the large morphological variability, use-wear traces reveal functional consistency and high levels of specialization for these tools. Almost all the use-wear traces we recorded developed from hide working with transverse motion. Moreover, we find no evidence that endscrapers were involved in the production of bone and antler tools during the late Protoaurignacian. Macroscopic and microscopic wear on the lateral edges of tools point to a considerable number of hafted endscrapers, which implies systematic time investment and planning depth. Comparison with the few endscrapers from transitional industries that have been analyzed highlights marked differences in the production, morphology, and use of these tools and reinforces our view of the Aurignacian as a complex not directly related with preceding European traditions.
The cultural dynamics that led to the appearance of the Aurignacian have intrigued archaeologists since the start of Paleolithic research. However, cultural reconstructions have often focused on a restricted region of Europe, namely the northern Aquitaine Basin. The Mediterranean Basin, though, is also a region worthy of consideration when testing if the Protoaurignacian was followed by the Early Aurignacian adaptive system. Fumane Cave is a pivotal site for tackling this issue because it contains evidence of repeated human occupations during the time span of the European Aurignacian. Here we investigate the diachronic variability of the lithic assemblages from five cultural units at Fumane Cave using a combination of reduction sequence and attribute analyses. This paper also reassesses the presence and stratigraphic reliability of the organic artifacts recovered at Fumane Cave. Our results show that the features of the Protoaurignacian techno-typology are present throughout the stratigraphic sequence, and by extension, to the onset of Heinrich Event 4. Additionally, the appearance of split-based points in the youngest phase is evidence of extensive networks that allowed this technological innovation to spread across different Aurignacian regions.
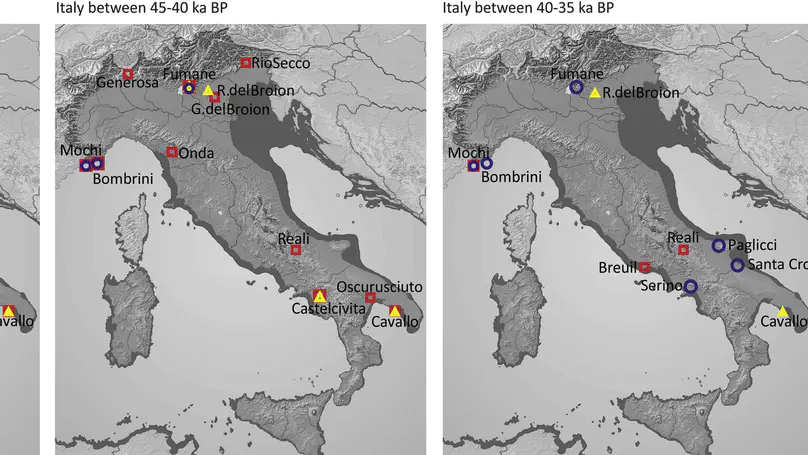
Defining the processes involved in the technical/cultural shifts from the Late Middle to the Early Upper Palaeolithic in Europe (~50-39 thousand years BP) is one of the most important tasks facing prehistoric studies. Apart from the technological diversity generally recognised as belonging to the latter part of the Middle Palaeolithic, some assemblages showing original technological traditions (i.e. Initial Upper Palaeolithic: Bohunician, Bachokirian; so called transitional industries: Châtelperronian, Szeletian, Lincombian-Ranisian-Jerzmanowician, Uluzzian; Early Upper Palaeolithic: Protoaurignacian, Early Aurignacian) first appear during this interval. Explaining such technological changes is a crucial step in order to understand if they were the result of the arrival of new populations, the result of parallel evolution, or of long-term processes of cultural and biological exchanges. In this debate Italy plays a pivotal role, due to its geographical position between eastern and western Mediterranean Europe as well as to it being the location of several sites showing Late Mousterian, Uluzzian and Protoaurignacian evidence distributed across the Peninsula. Our study aims to provide a synthesis of the available lithic evidence from this key area through a review of the evidence collected from a number of reference sites. The main technical features of the Late Mousterian, the Uluzzian and the Protoaurignacian traditions are examined from a diachronic and spatial perspective. Our overview allows the identification of major differences in the technological behaviour of these populations, making it possible to propose a number of specific working hypotheses on the basis of which further studies can be carried out. This study presents a detailed comparative study of the whole corpus of the lithic production strategies documented during this interval, and crucial element thus emerge: 1. In the Late Mousterian tools were manufactured with great attention being paid to the production phases and with great investment in inizializing and managing core convexities; 2. In contrast, Uluzzian lithic production proceeded with less careful management of the first phases of debitage, mainly obtaining tool morphologies by retouching. 3. In the Protoaurignacian the production is carefully organized and aimed at obtaining laminar blanks (mainly bladelets) usually marginally retouched. These data are of primary importance in order to assess the nature of the “transition” phenomenon in Italy, thus contributing to the larger debate about the disappearance of Neandertals and the arrival of early Modern Humans in Europe.
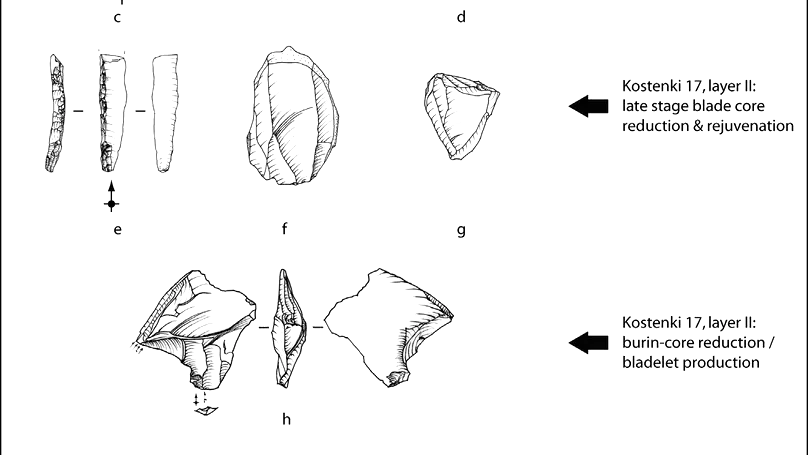
With great interest, we read the new study on early Upper Palaeolithic assemblages of the Kostenki region conducted by Dinnis et al. (2019). In this reply, we point out analytical and interpretative inconsistencies we found in that article. Dinnis et al. (2019) associated the early Upper Paleolithic (EUP) assemblages from the three Central Russian sites Kostenki 1, 14 and 17 with the Aurignacian four-phase model developed in Southwestern Europe. Thus, Dinnis et al. (2019) assigned the EUP assemblage from Kostenki 17 layer II to the Protoaurignacian and Kostenki 1/III as well as Kostenki 14/layer in volcanic ash (LVA; ~40 ka cal BP) to the Early Aurignacian. By doing so the authors promoted a unidirectional expansion of modern humans from the southeast into Europe.
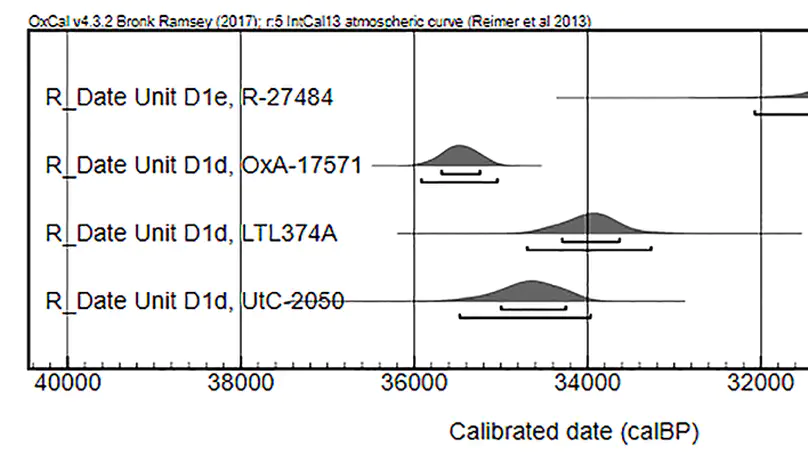
In Europe, the cultural trajectories of large-scale Upper Paleolithic cultural complexes, such as the Aurignacian and the Gravettian, represent highly debated topics. In this paper, we examine the evidence from the youngest anthropic layer D1d at Fumane Cave (Venetian Prealps, northeastern Italy) to investigate the nature of human settlement dynamics in the Great Adriatic-Padanian Region following the late Protoaurignacian cultural unit and before the advent of the Heinrich Event 3. We present an unusual charcoal feature unearthed during archaeological excavations and we conduct a careful techno-typological assessment of the lithic assemblage using a combination of reduction sequence analysis and attribute analysis. We thus explore the mode of occupation of the site and discuss the available radiocarbon dates on a regional and supra-regional scale. This study permits to assign layer D1d to the Gravettian as described in several sites south of the Alps and along the Italian peninsula. Moreover, the scarcity and general composition of the lithic assemblage supports the idea according to which human settlement at the edge of the Great Po Plain was sparse and intermittent in the early stages of this technocomplex. Finally, we address the early radiocarbon age estimation available for layer D1d and hypothesize different scenarios that need to be further explored.

The eighth annual meeting of the European Society of the Study of Human Evolution (ESHE) took place in Faro, Portugal, from September 13 to 15, 2018. The conference was hosted by the University of Algarve at the Campus de Gambelas (Portugal), with 300 registered participants attending. The society currently includes 378 professional and student members. With support from The Wenner-Gren Foundation, ESHE provided 36 applicants with travel grants or child care vouchers, and an additional 14 travel grants for scholars affiliated with African institutions.
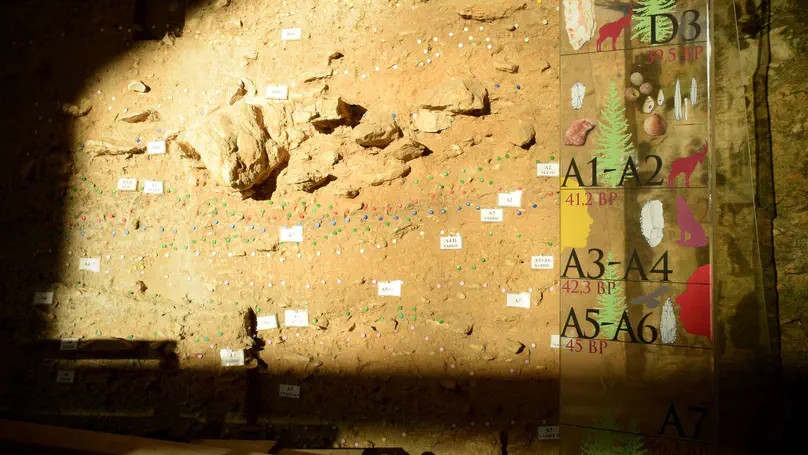

The Early Upper Paleolithic marks a turning point in the history of human evolution. Among the techno-complexes that characterize this period, the Aurignacian has received most of the attention because of its direct association with the spread of the modern humans into Europe. However, research has often neglected its important synchronic and diachronic variability. Regional studies and accurate re-evaluation of pivotal sites are thus fundamental in deconstructing the notion of the Aurignacian. This paper presents the results of an extensive techno-typological analysis of the lithic assemblages and a re-evaluation of the organic artifacts from five cultural units at Fumane Cave (Veneto, Italy). Furthermore, retouched bladelets from two Protoaurignacian sites, Isturitz (Basque Country, France) and Les Cottés (Vienne, France), are analyzed and compared to the record from Fumane Cave. The main research goals were to reassess the technological signature of the Protoaurignacian and examine the development of the Aurignacian in northern Italy to test whether the so-called “Aquitaine Model” can be applied to the whole European extent. Results of the empirical study and the inter-site comparison confirm that the Protoaurignacian is an industry dominated by bladelet implements, although lamellar production is based on a broad range of reduction strategies that are not related to the dwindling core dimensions as blade production progressed. Although rather homogeneous from a technological standpoint, the variability of retouched bladelets emphasizes the differences that exist between the Protoaurignacian regional groups. The study on the diachronic variability of the Aurignacian at Fumane Cave rejects the recurring practice, well-established among Paleolithic archaeologists, to transfer a regional model to geographically distant case studies. At Fumane Cave, the techno-typological features of the Protoaurignacian clearly persists throughout the stratigraphic sequence with some gradual variations that are less marked if compared to other sequences. Thus, both the “Aquitaine Model” and the idea according to which the Protoaurignacian vanished at the onset of the Heinrich 4 are invalidated when applied to northern Italy. In conclusion, this paper exemplifies how the re-evaluation of pivotal sites and the definition of regional signatures are able to yield new insights into the beginning and development of the European Upper Paleolithic.
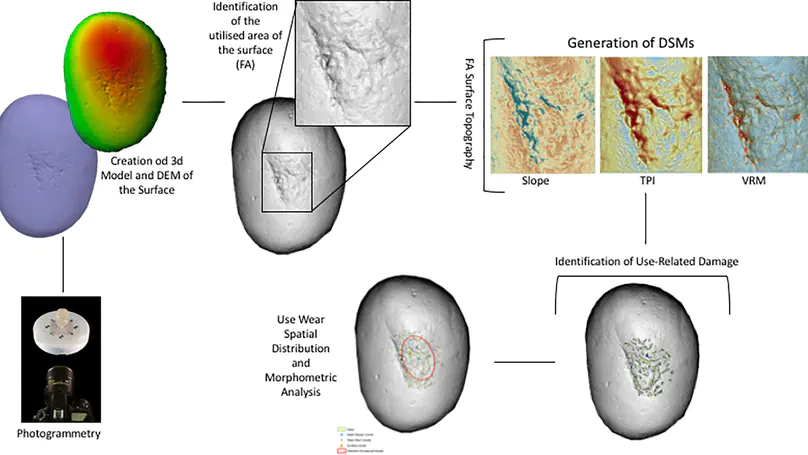
The article presents an original analysis which combines use-wear, 3D modelling and spatial analyses to experimental archaeology in order to investigate Early Upper Palaeolithic flint-knapping gestures and techniques involving the use of macro-lithic tools. In particular, the methodological framework proposed in this paper was applied to the study of Protoaurignacian and Aurignacian macro-tools from Fumane Cave (Verona, Italy). Combining spatial analysis and use wear investigation, both at low and high magnifications, permitted the identification and detailed description of the use-related traces affecting both the hammerstones and retouchers which, at Fumane Cave, were used at different stages during flint tool production. Several experimental activities were performed including core reduction, maintenance, and blank production together with different types of edge retouching. From a methodological perspective, the protocol of analysis permitted to codify specific traces and to produce quantitative data related to their geometry and distribution over the tool’s surface, according to the activities and gestures performed. The results obtained allowed a careful investigation of the function and the gestures associated to the use of the macro-lithic tools coming from the Protoaurignacian and Aurignacian levels of Fumane Cave while providing a methodological tool for interpreting different archaeological samples.
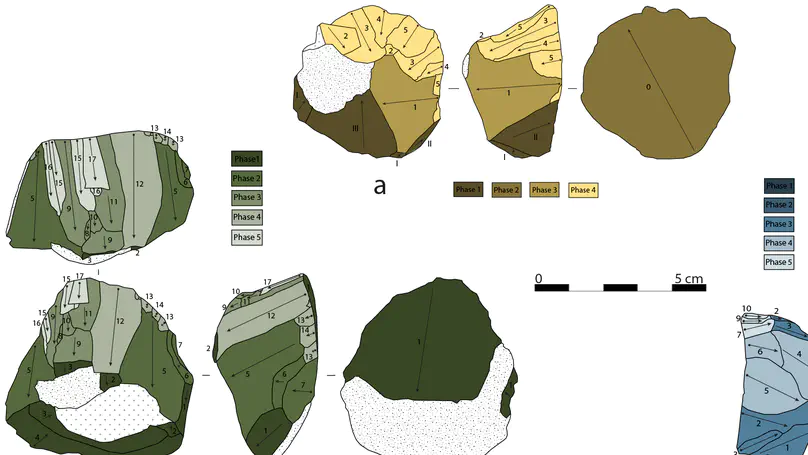
The Protoaurignacian is one of the European techno-complexes that marks the beginning of the Upper Paleolithic. During this time bladelet implements, frequently intended to be hafted in composite tools, become the primary goal of lithic production. The growing number of technological investigations carried out on several assemblages has revealed that, in most cases, bladelets are not the result of the reduction of blade cores. However, the detailed procedures involved in the production of blades and bladelets have rarely been reconstructed. Here we report on diacritic investigations of early stage and exhausted cores from the Protoaurignacian layers of Fumane Cave in northeastern Italy. We show that core reduction is influenced by two distinct operational concepts that relate to the manufacture of different predetermined products. The first is characterized by a linear and consecutive knapping progression that aims to obtain blades and, to a minor extent, bladelets with sub-parallel edges. The second is characterized instead by an alternated knapping progression that is exclusively used to produce slender bladelets with a convergent shape. We also show that carinated cores do not significantly differ, technologically, from semi-circumferential bladelet cores. We conclude by suggesting that there existed strong technological traditions shared between hunter–gatherers across the geographical extent of the Protoaurignacian.
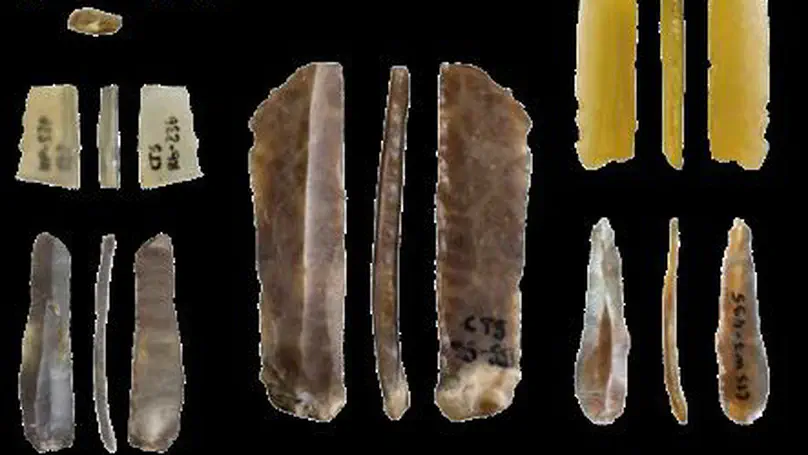

The Protoaurignacian is considered a cultural proxy for one of the first expansions of anatomically modern humans across Europe. The stabilization of bladelet industries that characterizes this techno-complex is therefore often used as supporting evidence for the break from previous stone knapping traditions and also for the increase of human mobility through wider territories. Despite the cultural importance that bladelets have gained, a careful inter-regional comparison, stressing similarities and differences, has not yet been attempted. Moreover, the use of traditional typologies has blurred the morpho-metrical variability that characterizes lamellar tools. Here, a study has been carried out on retouched bladelets from three pivotal sites: Fumane (northeast Italy), Isturitz (southwest France), and Les Cottés (northern France). By using morphological, dimensional, and retouching attributes, and by evaluating the statistical significance of the main differences, the first detailed analysis of the variability of retouched bladelets within the Protoaurignacian has been documented. The results indicate that the features that best discriminate the bladelet assemblages are the presence and the relative variability of bladelets with convergent retouch, although a reassessment of existing studies and new methodological approaches are required to test the latter hypothesis. Throughout this paper, we demonstrate the merits of using a unified classification of retouched bladelets for comparing behavior in between groups distant in space. We hope that this paper will be a new incentive to develop unified taxonomies for the study of Early Upper Paleolithic lithics in Western Eurasia.
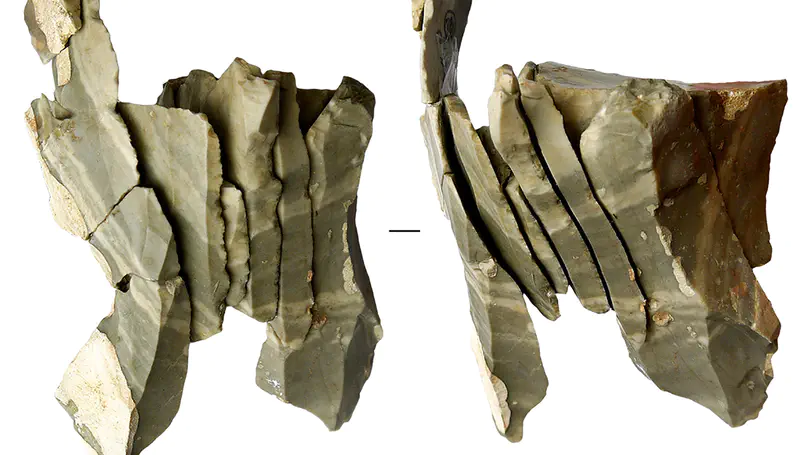

In the scenario of the spread of the anatomically modern humans (AMHs) into Europe, the techno-complex known as Protoaurignacian is defined by the production of blades and bladelets within a single and continuous stone knapping sequence from the same core as the result of its progressive reduction. However, the growing re-evaluation of some assemblages is revealing that bladelets are frequently obtained from independent reduction sequences, hence discouraging the direct application of the model developed in southwestern France. High-resolution regional signatures are thus needed to reconstruct a more accurate portrait of the AMH colonization dynamic. Northeastern Italy, with the key site of Fumane Cave, is one among the regions of Mediterranean Europe worthy of consideration for reconstructing this colonization process and its cultural dynamics. Within the framework of a critical discussion of the technological definition of the Protoaurignacian and its relationship with contemporaneous industries on a regional and supra-regional scale, we present the results of a detailed analysis of the lithic technology from units A2-A1 based on reduction sequence and attribute analyses. Results show that bladelets are the first goal of production and they do not originate from reduced blade cores but from a broad range of independent and simultaneous core reduction strategies. One implication is that the most commonly used technological trait that is said to define the Protoaurignacian has been over-emphasized and that the Protoaurignacian is technologically consistent across its geographical extent. Additional data based on carinated core technology imply that this techno-complex shares a common technological background with the Early Aurignacian and that no features are restricted to one of the two facies. Furthermore, the major difference between the Protoaurignacian and Early Aurignacian appears to be more typological in nature, with retouched bladelets being less common in the Early Aurignacian.